Knitting Process
Knitting process makes a two dimensional fabric structure by textile material with appropriate strength, elasticity, flexibility, etc., is used for various applications, especially clothing. Here in this process the continuous length of the yarn is converted into vertical intermeshed loop structure. According to the yarn insertion direction during loop construction, the knitting process can be divided as –
1. Weft knitting
2. Warp knitting.
Out of the two types, weft knitting is widely used in the knitting industry. In warp knitting process flat fabric is can be produce. But with weft knitting flat fabric as well as tubular fabric can be manufactured.
Let’s see basics of circular weft knitting process and it’s machine –
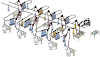
1. Circular Knitting Machine Parts
1 - Legs
2 - Cylinder
3 - Dial
4 - Needle
5 - Cam Parts
6 - Feeder guide
7 -Cam
8 - Supply Package
9 - Creel
10 - Top Stop motion
11 - Anti Snarl Device
12 - Tensioner
13 - Positive feeder
14 - Knitted fabric
15 - Fabric spreader
16 - Fabric withdrawal roller
17 - Fabric winding roller
2. Basic Terms in Knitting
1) Wales
Vertical lines of loops formed by one needle running parallel to the width of the fabric is known as wales.
2) Coarse
Horizontal lines of loops running perpendicular to the width of fabric is known as coarse.
3) Face loop
Face type of look is formed on face side of the fabric.
4) Back loop
Back loop is formed on back side of the fabric.
5) Stitch
To form a fabric by the intermeshing of loops of yarn.
6) Needle loop
Upper portion of loop is known as needle loop.
7) Sinker loop
Lower part of the loop is known as sinker loop.
8) Single jersey
In single jersey fabric all the loops are either formed by face loop or back loop.
9) Double jersey
Double Jersey fabric is made by some face loops and back loops. For this face loops are formed by one set of needle and back loops are formed by other set of needle. E.g. Rib, Interlock
10) Stitch length/loop length
11) Coarse length
Length of one complete coarse is the coarse length.
12) Open loop
When yarn is coming from one side and goes to other side without crossing to form a loop is called the open loop.
13) Closed loop
When yarn is coming from one side and goes to other side by crossing to form a loop is called the closed loop.
14) Stitch types
i. Knit
Yarn is completely raised to form a loop.
ii. Tuck
In tuck stitch yarn is partially raised to form a loop.
iii. Miss/float
Here yarn just passed without forming a loop.
15) Gauge
Gauge is nothing but number of needles in one inch or 25.4 mm. Indicates fineness of knit texture produced.
16) Pitch
Centre to centre distance between needles is known as pitch.
Lesser the gauge, less will be the pitch and vice versa.
17) Feeder density
It is numbers of feeder per inch diameter of the cylinder.
Feeder density = Total number of feeders/diameter of the cylinder (in inches)
18) Sinker
It is a divider blade which moves or pushes the yarn alternately between the needles. It acts as a loop-forming device in conjunction with the needle. Sinkers are generally placed at 90° to the needle bed. Also it holds the older loops at the bottom portion of the needle. Thus prevent the old loops from being lifted with needles as they rise to release them from their hooks.
19) Cam
Can is nothing but a path or track for the needle through which needle butt is operate. Their are various tracks for different stitches like knit, tuck, miss or float. This is how rising and lowering of needle is happen. Hence fabric design or construction depends on cam track.
3. Method Orientation (Modifications) in the knitted fabric
1) Using Coloured yarns
2) Horizontal stripes (Use of multi-coloured yarns)
3) Using various Yarn having different count
4) Variation in Twist (Low, high, twist direction)
5) Origin of yarn (Natural, man-made, regenerated)
6) Plating
7) Using Elastomeric yearns
8) Varying Stitch length
9) Dying of fabric
10) Printing of fabric
11) Various finishes e.g. softening, lustrous finish, etc.
12) Embroidery work
13) Use of different stitch
4. Applications of Knitted Fabric
Socks, upper storey, geotextile, agro textiles, filter fabrics, T shirts, net fabric, hand gloves, medical Textiles, undergarments, swimsuits Apparels, automotive textiles, etc.





















0 Comments
If you have any doubts, please don't hesitate to ask