Weaving Process in Textile Industry
The fabric is made on the weaving loom. The process of making fabric is called as weaving. Their are many types of looms like handloom (manual) and automatic loom like air jet, water jet, rapier, projectile, etc.
For weaving, beam preparation is mandatory. The beam is placed on the weaving loom and denting (yarn passing through the heald wires) is done. Then with the help of three primary motions fabric is made. Those primary motions are – 1) Shedding 2) Pick up 3) Beat up. These primary motions works in sequence with each other.
Beam preparation
Here many cheese packages are wound on the large beam known as warper beam. Later few warper beam are used to wound on a beam known as weaver beam. During this process a chemical size paste is applied to the yarns to increase their strength to bear the weaving process. This will reduce the breakages of yarns during weaving.
Sizing of yarns
During preparation of beam a chemical size paste is applied to the yarns to increase the strength of the yarns and thus to reduce the breakages during weaving process. So that warp yarns can withstand the complex stresses to which they are subjected in the weaving machine, they are strengthened by coating them with a thin film of size, and then drying.
The size is usually a starch paste containing softening and other ingredients. Starch sizes are usually not satisfactory for synthetic fibre threads and have to be replaced by special sizes (often containing synthetic polymers) which will adhere better to the thread.
Objective of Sizing –
1. To increase strength of the yarn.
2. To increase the abrasion resistance of yarns.
3. To reduce the hairiness that would cause problems in weaving process.
4. To reduce fluff and fly during the weaving process for high speed weaving machines.
Weaving process works on 3 primary motions –
1. Shedding
Shedding mechanisms convert the design instructions into the up and down movement of the heald frames. The lift of the heald frames can be achieved by using a cam or dobby mechanism. In the jacquard loom, there is no heald frame to be driven but each warp yarn is attached to a wire or cord.
Their are there main types of shedding mechanism
1) Tappet (Cam)
2) Dobby
3) Jacquard
Each mechanism has its own limitations. There are others mechanical or technical differences between these ways to add a difference to performance limitations.
2. Pick up
On conventional looms the filling yarn is inserted through the shed by means of a shuttle on which a pirn is mounted. As the shuttle travels a length of weft yarn is laid down along the path of the shuttle.
3. Beat up
A newly installed yarn or pick is pressed at great strength to the cloth with a reed wire.
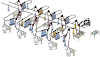
Here are some of the components of the weaving machine
1. Weaver beam
It supplies the warp yarns to the machine.
2. Heald wires
It use to hold the yard while weaving process. The warp yarns are passed through it and perform lifting motion.
3. Heald shaft
It holds all the heald wires. Their are minimum two heald shafts. This number can exceed more than 2. It helps in forming shed by lifting warp yarns, so that shuttle can go through it. Thus shedding is done by the heald shaft.
4. Shuttle
Shuttle is holding purn yarn (i.e. weft yarn) which moves from inside the shed form by shedding mechanism. This shuttle carries the responsibility of picking. As the shuttle travels a length of weft yarn is laid down along the path of the shuttle.
5. Reed shaft
Reed shaft is responsible for beat up motion. Newly transferred weft yarn is beat up by reed shaft to fix it with fabric.
6. Cloth roller
Cloth roller winds the weaved fabric.











0 Comments
If you have any doubts, please don't hesitate to ask